Dermato Surgery
All types of Dermato Surgeries are available in Skin 360 Clinic
Sebaceous Cyst
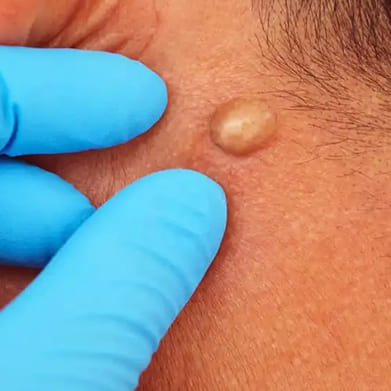
A sebaceous cyst, also known as an epidermoid cyst, is a noncancerous growth that develops beneath the skin. Here's a detailed explanation covering its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and complications:
- Causes: Sebaceous cysts form when the sebaceous glands, which produce oil (sebum) to lubricate the skin and hair, become blocked or damaged. This can occur due to trauma to the skin, follicular infundibulum obstruction, or hormonal changes.
- Symptoms: Sebaceous cysts typically appear as small, round lumps beneath the skin. They are usually firm to the touch and may be movable. The cysts are often painless but can become inflamed, infected, or tender if irritated or if bacteria enter the cyst.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis is usually based on the appearance of the cyst. Your healthcare provider may examine the cyst and may sometimes perform additional tests such as ultrasound or biopsy to rule out other conditions.
Mole / Wart / Corn
Alopecia is a medical term used to describe hair loss, which can occur in various forms and have different underlying causes. Here's a detailed explanation:
Moles:
- Description: Moles are small, dark spots or growths on the skin that are usually brown or black in color. They are caused by clusters of pigment-producing cells called melanocytes.
- Types: Moles can vary in size, shape, and color. They can be flat or raised, smooth or rough, and may appear alone or in groups.
- Causes: Moles can develop due to genetic predisposition, sun exposure, hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy), or a combination of these factors.
- Risk Factors: Individuals with fair skin, a history of sun exposure, or a family history of moles are at a higher risk of developing them.
- Monitoring: While most moles are harmless, it's essential to monitor them for changes in size, shape, color, or texture, as these could indicate melanoma, a type of skin cancer.
Warts:
- Description: Warts are small, rough growths caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) infecting the top layer of the skin.
- Types: There are several types of warts, including common warts (usually found on hands and fingers), plantar warts (on the soles of the feet), flat warts (small, smooth warts often found on the face), and genital warts (found in the genital and anal areas).
- Transmission: Warts are contagious and can spread through direct contact with an infected person or indirectly through contact with contaminated surfaces.
Corn:
- Description: Corns are thickened areas of skin that develop in response to pressure or friction, typically on the feet or toes.
- Types: There are two main types of corns: hard corns (which are small, concentrated areas of hard, thickened skin with a central core) and soft corns (which are softer and more moist, usually found between toes).
- Causes: Corns develop when pressure or friction irritates the skin, leading to thickening and hardening in the affected area. This can be caused by ill-fitting shoes, repetitive motion, or abnormal foot anatomy.
- Symptoms: Corns may cause pain, tenderness, or discomfort, especially when pressure is applied.
In summary, moles, warts, and corns are common skin conditions with distinct characteristics, causes, treatments, and preventive measures. It's essential to understand these conditions to effectively manage and prevent them. If you have any concerns about your skin or notice any unusual changes, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
Scar Revision
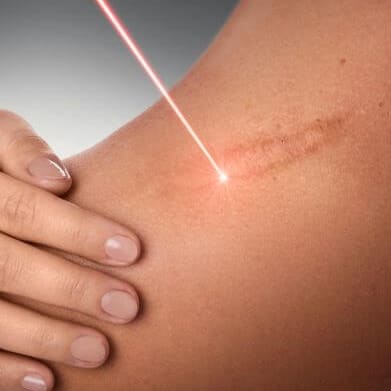
Scar revision is a medical procedure aimed at improving the appearance of scars, whether they are caused by injury, surgery, burns, or other factors. The goal of scar revision is not to completely remove the scar but to minimize its visibility and improve its texture.
- Assessment and Consultation: Before undergoing scar revision, a patient will typically consult with a dermatologist, plastic surgeon, or other qualified healthcare provider. During this consultation, the provider will assess the scar's size, location, depth, and type to determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
- Types of Scars: Scars can vary widely in appearance and characteristics. Common types of scars include:
- Hypertrophic scars: Raised, red, and thickened scars that remain within the boundaries of the original wound.
- Keloid scars: Similar to hypertrophic scars but extend beyond the boundaries of the original wound.
- Atrophic scars: Indented or depressed scars often caused by acne or other skin conditions.
- Contracture scars: Tight, pulled-together scars that can result from burns or large wounds.
Vitiligo Surgery
Vitiligo surgery refers to various surgical techniques aimed at repigmenting areas of the skin affected by vitiligo, a condition characterized by depigmented patches due to the loss of melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells. Several surgical methods exist, including:

- Autologous Skin Grafting: In this procedure, healthy skin is harvested from another part of the body and transplanted onto depigmented areas. The donor skin can be taken from areas unaffected by vitiligo, such as the buttocks or thighs. This technique is most effective for small patches of vitiligo.
- Punch Grafting: This involves taking small round sections of healthy skin using a tool called a punch biopsy. These grafts are then placed onto depigmented areas. This technique is suitable for smaller patches of vitiligo.
- Split-thickness Skin Grafting: This method involves removing a thin layer of skin from a donor site, such as the thigh, and placing it onto depigmented areas. It allows for larger areas of vitiligo to be treated but may result in a noticeable color difference between the grafted skin and surrounding skin.
- Microskin Grafting: This technique involves harvesting very tiny pieces of skin, often using a special tool called a dermatome, and transplanting them onto depigmented areas. The advantage of microskin grafting is that it provides a more natural appearance, especially for facial vitiligo.
- Suction Blister Grafting: This innovative technique involves creating blisters on healthy pigmented skin by applying suction. The roof of the blister, containing melanocytes, is then harvested and transplanted onto depigmented areas.
- Melanocyte Transplantation: In this method, melanocytes are extracted from a small section of healthy skin and then cultured in a laboratory to increase their numbers. These cultured melanocytes are then transplanted onto depigmented areas. This technique allows for a more targeted and precise repigmentation.
- Laser Therapy Combined with Surgery: Laser treatments such as excimer laser therapy may be used in combination with surgical techniques to enhance repigmentation and improve the results of surgery.
It's important to note that while surgical treatments for vitiligo can be effective in repigmenting the skin, they carry risks such as scarring, infection, and uneven pigmentation. Additionally, not all patients are suitable candidates for surgery, and the choice of technique depends on factors such as the extent and location of vitiligo, skin type, and individual preferences. Therefore, it's crucial to consult with a dermatologist or a specialist experienced in treating vitiligo to determine the most appropriate treatment approach for your specific case.
Nail Surgery
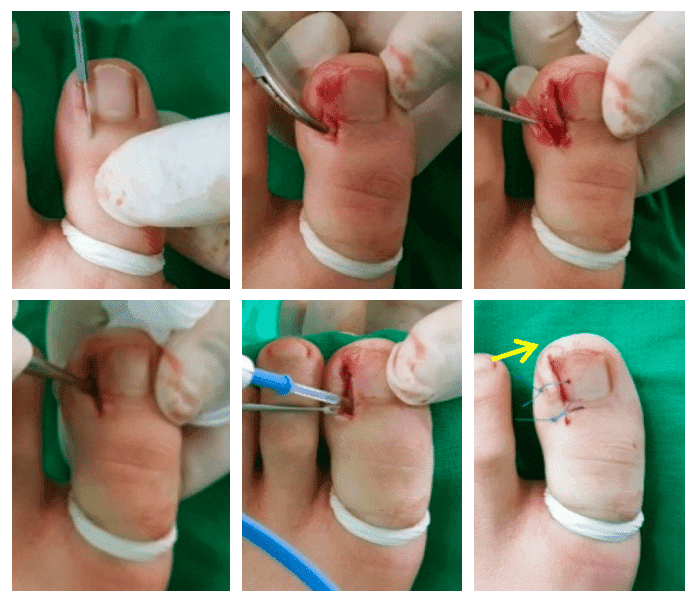
Nail surgery, also known as nail avulsion or nail removal surgery, is a medical procedure performed to treat various nail conditions that cannot be resolved through conservative treatments. Here is a detailed explanation of the procedure:
Indications for Nail Surgery:
- Ingrown toenails: When the edge of the nail grows into the surrounding skin, causing pain, inflammation, and possible infection.
- Chronic nail infections: Persistent fungal or bacterial infections that do not respond to medications.
- Trauma: Severe nail injuries or deformities resulting from accidents or repetitive trauma.
- Nail disorders: Chronic conditions such as pincer nails, in which the sides of the nail curve inward excessively, causing discomfort.
Pre-operative Evaluation:
- A thorough examination of the affected nail(s) and surrounding tissue.
- Discussion of the patient's medical history, current medications, and any allergies.
- Assessment of the patient's overall health to ensure they are suitable candidates for surgery
- Pre-operative instructions, including fasting requirements and cessation of certain medications.
Anesthesia:
- Nail surgery can be performed under local anesthesia, typically administered via injection to numb the affected area
- In some cases, sedation or general anesthesia may be used, especially if the procedure is extensive or the patient is anxious.
Recovery and Long-term Outlook:
- Most patients experience significant improvement in symptoms after nail surgery.
- Full recovery may take several weeks to months, depending on the extent of the procedure and individual healing factors.
- Patients are advised to follow their surgeon's instructions carefully to optimize healing and reduce the risk of complications.
- Long-term outcomes are generally favorable, with many patients experiencing resolution of their nail problems and improved quality of life.
Ear Lobe Repair
Ear lobe repair is a cosmetic surgical procedure aimed at correcting deformities, tears, or stretching of the ear lobes. Here's a detailed explanation:
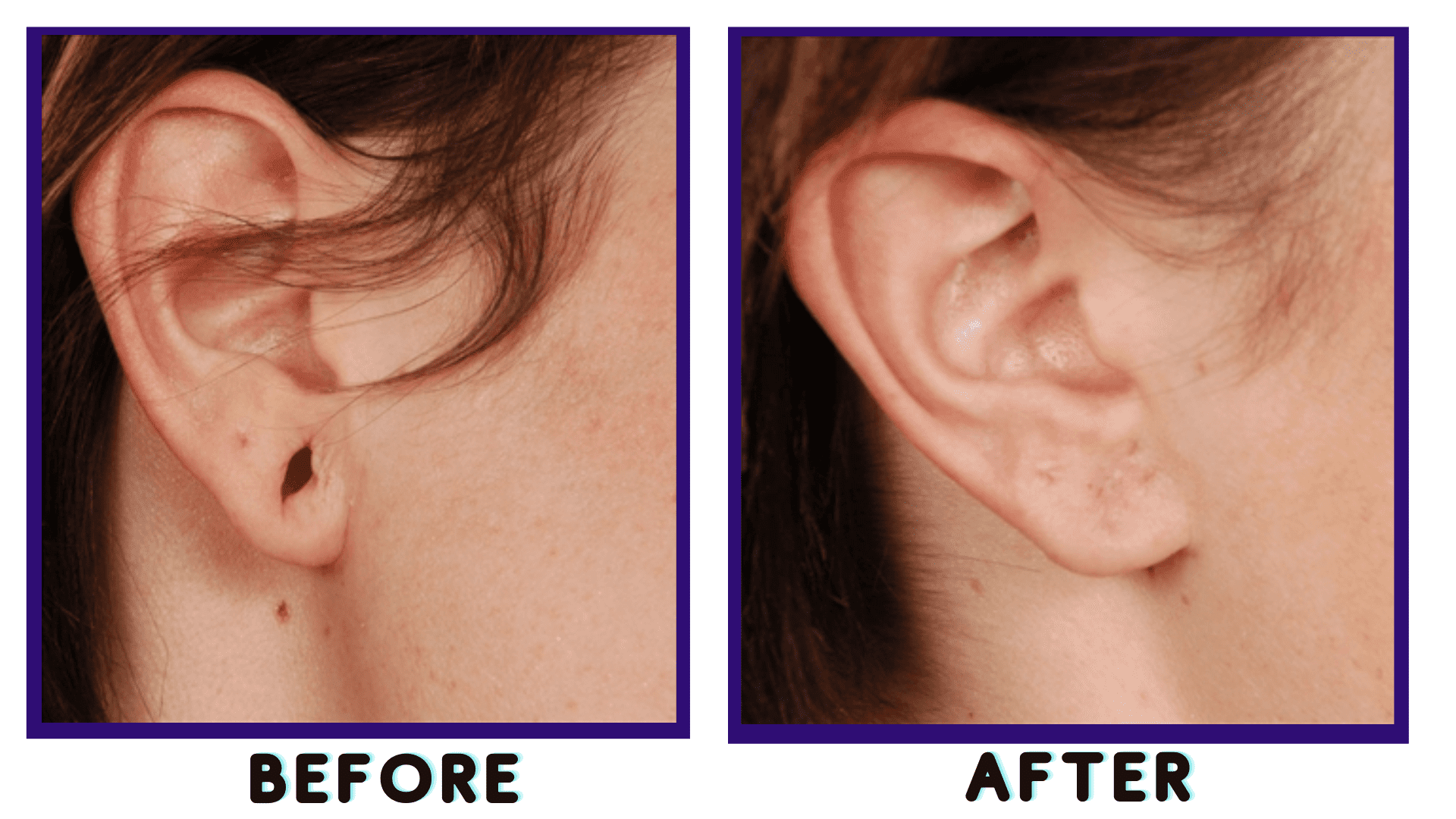
Causes of Ear Lobe Damage:
- Trauma: Tears or stretching due to accidents, piercings, or jewelry.
- Aging: Loss of elasticity in the skin leading to sagging or elongation of the ear lobes.
- Gauging: Stretching the ear lobes intentionally for fashion with large earrings or plugs.
Evaluation and Consultation:
- A consultation with a qualified plastic surgeon or dermatologist is crucial.
- The surgeon will assess the extent of damage, discuss patient goals, and explain the procedure.
Preparation:
- Before the procedure, patients may be advised to stop smoking and avoid certain medications that can increase bleeding.
- The surgeon will provide instructions on pre-operative care and what to expect during and after the procedure.