Laser Treatements
All types of Laser Treatments are available in Skin 360 Clinic

Hair Removal
Hair removal is a practice dating back to ancient times, with various methods employed to achieve smooth, hair-free skin. Here's a detailed explanation covering different methods, their mechanisms, benefits, and potential drawbacks:
- Laser Hair Removal: This method uses concentrated beams of light to target hair follicles, damaging them to inhibit future hair growth. Laser hair removal offers long-lasting results and can be used on larger areas of the body. It's relatively painless compared to other methods and may cause mild redness or swelling temporarily. Multiple sessions are usually required for optimal results.
Tattoo Removal
Tattoo removal is a process to eliminate unwanted tattoos from the skin. There are several methods available, each with its own advantages and considerations:

- Laser Removal: This is the most common and effective method. It involves using high-intensity lasers to break down the ink particles in the tattoo. The body's immune system then gradually removes the fragmented ink over time. Multiple sessions are usually required for complete removal, with the number depending on factors such as tattoo size, ink colors, and skin type.
- Intense Pulsed Light (IPL): Similar to laser removal, IPL uses light energy to target and break down tattoo ink particles. However, IPL devices emit a broader spectrum of light than lasers, which can make them less effective for certain ink colors and may require more sessions.
- Surgical Removal: For smaller tattoos, surgical excision involves cutting out the tattooed skin and stitching the surrounding skin together. This method is fast but may leave a scar, and it's not suitable for larger tattoos.
- Dermabrasion:This method involves mechanically sanding down the skin to remove the tattoo ink. It's an older technique that's less commonly used today due to its high risk of scarring and uneven results.
- Chemical Peel: Chemical peels involve applying a solution to the skin to remove the top layers, including the tattoo ink. This method is also less common and may result in scarring or pigmentation changes.
- Creams and Topicals: Various creams and topical treatments claim to fade or remove tattoos gradually. However, their effectiveness is limited, and they often require long-term use with uncertain results.
Factors to Consider:
- Tattoo Size and Color: Larger tattoos and those with multiple colors may require more sessions for complete removal.
- Skin Type: Skin tone and type can affect the effectiveness of certain removal methods and the risk of complications such as scarring or pigmentation changes.
- Location: Tattoos on certain parts of the body may be more difficult to remove due to differences in skin thickness and sensitivity.
- Health Considerations: Certain medical conditions and medications may affect the suitability of tattoo removal treatments. It's essential to consult a qualified dermatologist or tattoo removal specialist for personalized advice.
Overall, tattoo removal is a gradual process that requires patience and multiple sessions. It's essential to choose a reputable and experienced provider to minimize the risk of complications and achieve the best possible results.
Face & Body Pigmentation
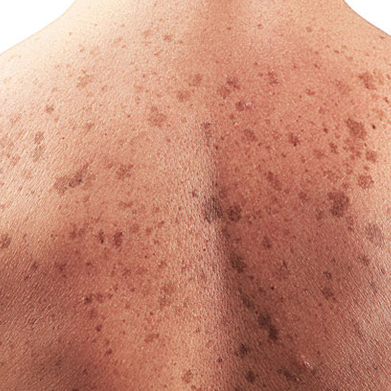
Pigmentation refers to the coloring of the skin, which is determined by the presence of a pigment called melanin. Melanin is produced by specialized cells called melanocytes, which are located in the basal layer of the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. The amount and distribution of melanin determine a person's skin color, which can vary widely among individuals.
Types of Pigmentation:
- Normal Pigmentation: This refers to the natural coloring of the skin, which varies depending on genetics, sun exposure, and other factors. People with darker skin tones generally have more melanin, while those with lighter skin tones have less melanin.
- Hyperpigmentation: This occurs when there is an overproduction of melanin, leading to dark patches or spots on the skin. Hyperpigmentation can be caused by factors such as sun exposure, hormonal changes (e.g., pregnancy or birth control pills), skin trauma (e.g., acne or injury), or certain medical conditions.
- Hypopigmentation: This refers to a decrease in melanin production, resulting in lighter patches or spots on the skin. Hypopigmentation can be caused by conditions such as vitiligo, a skin disorder where melanocytes are destroyed, or certain medications or treatments.
Stretch And Birth Marks
Stretch marks and birthmarks are common skin conditions that many people experience at some point in their lives. Here's a detailed explanation of each:
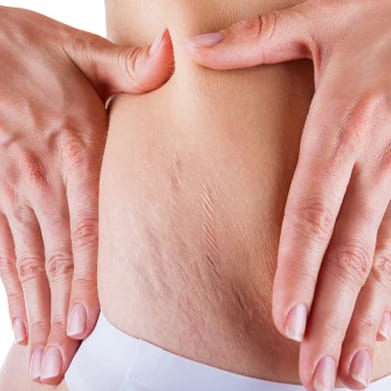
Stretch Marks (Striae):
- Definition: Stretch marks, medically known as striae, are narrow streaks or lines that develop on the skin's surface. They often appear as slightly raised, discolored bands, ranging from pink to purple initially and fading to silvery-white over time.
Causes:
- Rapid stretching of the skin due to growth spurts during puberty, pregnancy, or rapid weight gain.
- Hormonal changes, such as during puberty or pregnancy, can weaken the skin's elasticity.
- Genetics can also play a role in susceptibility to stretch marks.
Locations: Common areas where stretch marks occur include the abdomen, hips, thighs, buttocks, breasts, and upper arms.
Birthmarks:
Definition: Birthmarks are irregularities on the skin that are present at birth or develop shortly afterward. They vary in size, shape, color, and texture and can be classified into two main types: pigmented birthmarks and vascular birthmarks.
Types:
- Pigmented Birthmarks: These birthmarks are caused by an overgrowth of pigment cells and include moles, cafe-au-lait spots, and Mongolian spots.
- Vascular Birthmarks: These birthmarks result from abnormal blood vessels and include port-wine stains, hemangiomas, and stork bites.
Causes:
- The exact cause of birthmarks is often unknown, but they can result from genetic factors, abnormal blood vessel development, or an overproduction of pigment cells.
Acne Scars
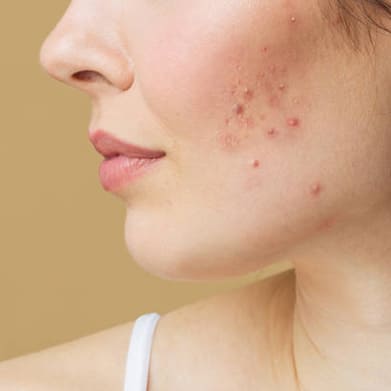
Acne scars are the result of inflammatory acne lesions, such as papules, pustules, and cysts, damaging the skin tissue. There are several types of acne scars, including atrophic scars (such as icepick, boxcar, and rolling scars) and hypertrophic or keloid scars.
Causes of Acne Scars:
- Acne scars occur when the body's natural healing process is disrupted during severe acne outbreaks. Inflammatory acne lesions damage the skin's collagen and elastin fibers, leading to irregular healing and scar formation.
Types of Acne Scars:
- Atrophic Scars: These are depressions in the skin and include icepick, boxcar, and rolling scars.
- Icepick scars: Small, deep pits that extend into the dermis.
- Boxcar scars: Broad, depressed scars with sharply defined edges.
- Rolling scars: Wide depressions with a wave-like appearance.
- Hypertrophic or Keloid Scars: Raised scars that develop when the body produces too much collagen during the healing process.
Prevention of Acne Scars:
- Treat acne promptly and effectively to minimize inflammation and reduce the risk of scarring.
- Avoid picking, squeezing, or popping acne lesions, as this can worsen inflammation and increase the likelihood of scarring.
- Use non-comedogenic skincare products to prevent clogged pores and new acne breakouts.
- Protect the skin from sun exposure, as UV radiation can worsen hyperpigmentation and delay the healing of acne scars.