Skin Diseases
Cure from all type of Skin Diseases
Skin Infection
Skin infections encompass a broad range of conditions caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites invading the skin, leading to symptoms such as redness, swelling, pain, and sometimes pus formation; treatments vary depending on the causative agent and severity, often requiring antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, or other medications, along with proper wound care and hygiene practices to prevent further spread or complications.
Symptoms Of Skin Infection
Skin infections can manifest with a variety of symptoms including redness, swelling, warmth, pain, itching, rash, pus or fluid-filled blisters, fever, and in severe cases, systemic symptoms like fatigue or malaise. Specific symptoms depend on the type of infection, whether bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic, and can range from localized to widespread involvement. It's crucial to seek medical attention if you suspect a skin infection for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Skin Allergies
Skin allergies occur when the immune system reacts to substances that are typically harmless, resulting in symptoms such as itching, redness, swelling, or rash upon contact with allergens like certain foods, plants, chemicals, or materials.
Treatment may involve avoiding triggers, using topical or oral medications, and in severe cases, seeking medical intervention for allergy management.
Symptoms Of Skin Allergies
Symptoms of skin allergies can vary depending on the type of allergy and individual sensitivity, but common signs include itching, redness, swelling, rash, hives, blistering, dryness, or flakiness of the skin. In severe cases, symptoms may progress to oozing, crusting, or even blistering. Allergic reactions can occur immediately upon contact with the allergen or develop gradually over time with repeated exposure.
Here are some major symptoms of Skin Allergies :
- Itching
- Redness
- Swelling
- Rash
- Hives (raised, itchy bumps)
- Dry, scaly skin
- Blisters
- Peeling or flaking skin
- Warmth or tenderness in the affected area
- Pain or discomfort
Acne
Acne is a common skin condition characterized by the occurrence of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, cysts, and nodules primarily on the face, chest, back, and shoulders. It typically arises during puberty due to hormonal changes but can affect individuals of all ages. The main causes include excess oil production, clogged hair follicles, bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes), hormonal fluctuations, genetics, certain medications, and lifestyle factors such as diet and stress.
Types Of Acne Include
- Comedonal Acne: Characterized by blackheads and whiteheads.
- Inflammatory Acne: Includes papules (small red bumps), pustules (pus-filled lesions), nodules (painful, solid lumps beneath the skin), and cysts (large, painful, pus-filled lumps beneath the skin).
Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed patches of skin. It is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
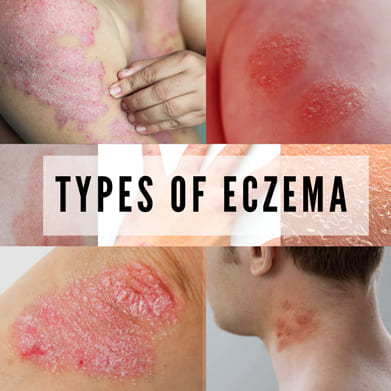
Eczema can vary in severity and may flare up periodically. Common triggers include irritants (such as soaps, detergents, and certain fabrics), allergens (such as pollen, pet dander, and dust mites), extreme temperatures, stress, and hormonal changes. Treatment typically involves moisturizing the skin regularly, avoiding triggers, using topical corticosteroids or other anti-inflammatory medications to reduce inflammation, and managing itching with antihistamines or other medications. In severe cases, phototherapy or systemic medications may be prescribed by a healthcare professional. Eczema cannot be cured, but with proper management, symptoms can be controlled effectively, allowing individuals to lead normal lives.
Symptoms Of Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, presents a range of symptoms which may vary in severity and appearance. Common symptoms include:
- Itching (pruritus): Often intense and persistent itching, which can worsen with scratching, leading to skin damage and infection.
- Redness (erythema): Inflamed and irritated skin, typically appearing as patches or areas of redness.
- Dryness: Skin affected by eczema tends to be dry, rough, and may develop scaling or flaking.
- Rash: Eczema can cause a rash that may be raised or flat, with distinct borders. It often appears in patches, commonly on the face, hands, feet, knees, elbows, or other areas where skin folds.
- Cracks: Skin affected by eczema can develop small cracks, which may be painful and prone to infection.
- Blistering: In severe cases, eczema may lead to the formation of small fluid-filled blisters, which can ooze and crust over.
- Discoloration: Prolonged inflammation may lead to changes in skin color, appearing lighter or darker than the surrounding skin.
- Secondary infections: Scratching can break the skin barrier, increasing the risk of bacterial, viral, or fungal infections.
Psoriasis
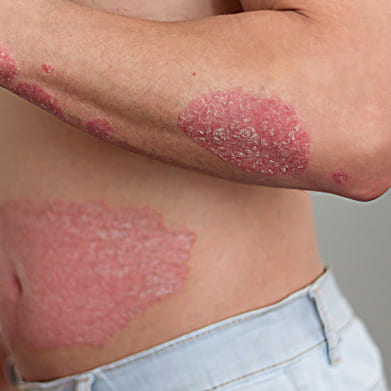
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by rapid skin cell turnover, leading to the buildup of thick, scaly patches on the skin's surface. It is caused by a faulty immune response that triggers inflammation and excessive skin cell production. Symptoms include red, inflamed patches covered with silvery scales, itching, and sometimes pain. Psoriasis can affect any part of the body, including the scalp, elbows, knees, and nails, and it may also be associated with other health conditions such as psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and depression. Treatment options include topical creams, oral medications, phototherapy, and biologic drugs, aimed at reducing inflammation, slowing skin cell growth, and managing symptoms. It's a lifelong condition with periods of flare-ups and remission, and while there's no cure, effective management strategies can help control symptoms and improve quality of life.
Symptoms And Cure Of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches of skin caused by an overactive immune system triggering excessive skin cell growth. Symptoms include red patches of skin with silvery scales, dryness, itching, and sometimes pain.
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a long-term skin condition characterized by patches of skin losing their pigment. The exact cause is unclear but believed to involve autoimmune, genetic, and environmental factors.
It can affect any area of the body and can be emotionally distressing due to its noticeable appearance.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), also known as sexually transmitted infections (STIs), are infections spread through sexual contact. They can be caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites, or fungi and may affect the genitals, rectum, mouth, or throat. Common STDs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, HIV/AIDS, herpes, HPV (human papillomavirus), and trichomoniasis.
Transmission typically occurs during vaginal, anal, or oral sex, as well as through sharing of infected needles or from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding. Many STDs can be asymptomatic, meaning individuals may not display any symptoms, which increases the risk of unknowingly transmitting the infection to others. However, symptoms may include genital sores, abnormal discharge, pain during urination, itching, and pelvic pain.
Prevention strategies include practicing safe sex through consistent and correct condom use, limiting sexual partners, getting vaccinated for preventable infections like HPV, and undergoing regular STD testing, especially for those who are sexually active or have multiple partners. Prompt treatment with antibiotics or antiviral medications can effectively manage many STDs, although some, such as HIV and herpes, have no cure but can be managed with antiretroviral therapy or antiviral medications, respectively.
Education, open communication with sexual partners, and seeking medical advice when necessary are crucial components of STD prevention and management.
Symptoms Of Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) can manifest with a wide range of symptoms, varying based on the specific infection. However, many STDs may initially present with no symptoms at all, making regular testing crucial for early detection and treatment. Common symptoms of STDs include:
- Unusual Discharge: Thick, cloudy, or bloody discharge from the penis or vagina may indicate an infection such as gonorrhea or chlamydia.
- Pain or Burning Sensation: Pain or discomfort during urination or intercourse can be a sign of various STDs, including gonorrhea, chlamydia, or genital herpes.
- Genital Sores or Ulcers: Open sores, blisters, or ulcers in the genital area may be caused by infections such as genital herpes, syphilis, or chancroid.
- Genital Itching or Irritation: Persistent itching, redness, or irritation in the genital region may indicate the presence of an STD, such as pubic lice (crabs) or trichomoniasis.
- Rash or Lesions: STDs like syphilis, HIV, and herpes can cause skin rashes, lesions, or bumps on the genitals or other parts of the body.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Enlarged or tender lymph nodes in the groin area or elsewhere may be a sign of an underlying infection, including HIV or syphilis.
Drug Reaction
Drug reactions, also known as adverse drug reactions (ADRs), encompass a range of unexpected and undesirable effects that occur after taking medication. These reactions can vary in severity, ranging from mild side effects like nausea or dizziness to severe allergic reactions or organ damage.
There are several types of drug reactions:
- Allergic reactions: These occur when the body's immune system mistakenly identifies the drug as harmful and mounts an immune response. Symptoms can range from mild itching or rash to severe anaphylaxis, which can be life-threatening.
- Side effects: These are unintended and often predictable effects of a medication. They can include nausea, drowsiness, headache, or changes in appetite. Side effects vary depending on the drug and individual factors such as age, health status, and genetic makeup.
- Drug interactions: Some medications can interact with each other, altering their effectiveness or causing unexpected side effects. This can occur when drugs have similar mechanisms of action or affect the same metabolic pathways in the body.
- Toxic reactions: These occur when a drug accumulates in the body to toxic levels, leading to adverse effects. This can happen due to factors such as overdose, impaired drug metabolism, or underlying medical conditions that affect drug clearance.
- Idiosyncratic reactions: These are rare and unpredictable reactions that occur in certain individuals but not others. They may be caused by genetic factors or unknown mechanisms.